Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Defibrillation (CRT-D)
For patients with heart failure who are getting cardiac resynchronization therapy and considering defibrillation
What is CRT?
Sometimes the heart pumps poorly. In other words, the heart beats out of sync. This can be caused by damage to the heart, age, genetics, certain medicines, and other reasons. CRT helps the heart pump normally by helping the right and left ventricles of the heart pump together. To do this, special wires are placed in the heart to pace the heart muscle in a specific way that improves the pumping function.
Your Decision
You and your doctor can decide together if you would like to have a CRT implantation to help treat your heart failure. However, there is another important part of this decision. Patients with heart failure may be at risk for sudden dangerous heart rhythms. These heart rhythm abnormalities may be life-threatening, and in some cases can cause a cardiac arrest. The best treatment for these dangerous heart rhythms is a “defibrillator.” This is a device that can sense these heart rhythms and deliver a shock to your heart if you need it. CRT can be combined with a defibrillator. This combination is sometimes abbreviated “CRT-D.”
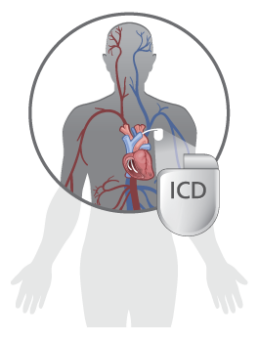
What is a CRT-D?
A CRT-D is a small device that combines cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillation. It is placed under the skin of the chest. Wires (called “leads”) connect the CRT-D to the heart. A CRT-D is designed to prevent an at-risk person from dying suddenly from a dangerous heart rhythm. CRT-Ds sense dangerous rhythms and treat them right away. The CRT-D uses pacing or an electrical shock to stop a dangerous heart rhythm and change it to a normal heart rhythm. This happens much faster than a person could get to the hospital for treatment.
Considering CRT with defibrillation FAQ's
Yes, the CRT-D is put under the skin and one or more wires (called “leads”) are put into the heart. The surgery takes a few hours. You may stay in the hospital overnight
The defibrillator will not make you feel better. However, the cardiac resynchronization therapy may make you feel better.
2 out of every 100 patients will have a serious problem like damage to the lung or heart.
About 1 out of every 100 patients will develop an infection.
Some patients develop anxiety or depression from being shocked.
Patients say that getting shocked is like “being kicked in the chest.” Some patients pass out before they are shocked and do not remember being shocked. Before a shock is delivered, the CRT-D will try to correct your dangerous heart rhythm.
You may survive a dangerous heart rhythm only if you are treated within a few minutes with an external shock. However, many patients die before emergency help can reach them.
Without a CRT-D: Patients without a CRT-D are more likely to die suddenly from a dangerous heart rhythm. Without a CRT-D, over 5 years, 36 out of every 100 patients with heart failure will die over a 5-year period.
With a CRT-D: Patients with a CRT-D are less likely to die suddenly of a dangerous heart rhythm. With a CRT-D, 29 out of every 100 patients with heart failure will die over a 5-year period. This means 7 more patients would live with a CRT-D over a 5-year period.
Supporting Evidence
Here is a document outlining all evidence for practice decision aids, to help you in your decision.
